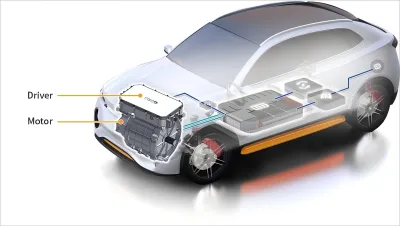
Low-Voltage Products: Thermal Pads, Flexible Adaptation Protects Precision Components
Low-voltage motor controllers are primarily used in low-power commercial vehicle scenarios (e.g., small electric trucks, light-duty operational vehicles, etc.). Their internals concentrate precision electronic components like chips and sensors. These components generate heat evenly but have lower power density, yet they demand high insulation, sealing, and conformability from the thermal material. Traditional metal heat sinks can easily scratch components and struggle to conform to curved surfaces, while ordinary thermal paste tends to dry out and offers poor insulation.Thermal pads use silicone as a base. By adding thermally conductive fillers (such as alumina, boron nitride, etc.), they can achieve thermal conductivity ranging from 1-15 W/(m·K), allowing flexible selection based on the heat dissipation needs of different components. They fill the gaps between components and the heat sink shell, facilitating smoother heat transfer, and their elasticity helps buffer vibrations to protect components. They offer superb insulation, can withstand voltages over 20kV, have high resistivity, balancing thermal conduction and insulation to meet low-voltage safety requirements.
High-Voltage Products: Thermal Grease Paired with Insulating Film, A Golden Combo for Strong Heat Dissipation
High-voltage motor controllers are mostly used in high-power commercial vehicle scenarios (e.g., heavy-duty trucks, large buses, etc.). Their core consists of power modules like IGBTs and MOSFETs. Under high current, heat generation is concentrated, with local temperatures exceeding 125°C. Furthermore, the high-voltage environment carries a high risk of insulation breakdown, making it difficult for a single material to address both heat dissipation and insulation.Thermal grease is a key thermal interface material for high-voltage motor controllers. Its thermal conductivity exceeds 3.0 W/(m·K), enabling it to quickly transfer heat to the cooling fins. It has good fluidity and wettability, can fill imperfections on metal contact surfaces, eliminating air barriers, and operates stably between -50°C and 200°C, adapting to extreme temperature variations.
The Thermal conductive insulating film serves as the core insulation guarantee for high-voltage motor controllers. Based on fiberglass cloth coated with silicone rubber, it has an insulation strength exceeding 15kV/mm, withstands temperatures over 200°C, and is also resistant to chemical corrosion and is flame retardant. Placed between the power module and the heat sink shell, it both blocks high-voltage arcs and works in tandem with thermal grease to form a dual guarantee of "thermal conduction + insulation".
Select the Right Material for the Right Zone, Ensuring Stable Operation in Complex Conditions
Commercial vehicles operate year-round in urban and rural road conditions, facing multiple challenges including continuous vibration, extreme temperature variations from -30°C to 60°C, and erosion by dust and oil contamination. Thermal materials must not only meet performance standards but also possess strong environmental adaptability.In low-voltage motor controllers, thermal pads, relying on a compressibility of 30%-70%, can maintain close contact with components even during continuous vehicle jolting, avoiding the heat dissipation failure caused by gaps forming due to vibration with traditional rigid materials. Addressing the extreme temperature challenge in high-voltage motor controllers, 3W thermal grease employs special viscosity control technology to remain unfrozen at -50°C and non-sagging at 150°C, while the insulating film maintains stable insulation performance. Simultaneously, the thermal materials for both product types have all passed IP6K9K resistance to washout tests, ensuring long-term use in dusty and oily environments without affecting thermal and insulation performance.
Sheen's zoned thermal solution, through scenario-specific precision design, can effectively reduce motor controller failure rates by over 30% and extend service life to 8 years / 300,000 kilometers or more, providing reliable power guarantee for commercial vehicles with different power needs.

 English
English
 usheenthermal
usheenthermal




