How-To Guide: Choosing Between Thermal Pads vs Thermal Paste
Choosing between thermal pads vs thermal paste can feel like picking the lesser evil in a sweaty tech showdown—one’s clean and convenient, the other’s messy but mighty.
“Thermal interface materials will account for over $2.8 billion in global spending by 2026,” according to MarketsandMarkets. That tells you one thing: this stuff matters—a lot more than most folks give it credit for.
Key Factors to Consider: Thermal Pads vs Paste
Understanding Thermal Conductivity Performance in Thermal Pads and Paste
- Thermal conductivity is king here. Measured in Watt per meter-Kelvin (W/mK), it tells us how fast heat moves through a material.
- Sheen Technology's newly launched graphene thermal pad boasts a thermal conductivity of up to 70W/mK.
Thermal Resistance: How Different Materials Impact Efficiency
- Lower thermal resistance means faster cooling.
- Pastes fill microscopic gaps more completely, reducing air pockets.
- Pads offer consistency but can leave micro-gaps if not compressed properly.
Electrical Insulation: The Role of Thermal Interface Materials
- Most thermal pads are naturally non-conductive—great news if you're working around sensitive PCBs or VRMs.
- Some pastes contain metal particles like silver or aluminum oxide, which can conduct electricity—watch out!
Operating Temperature Range: Choosing the Right Material for Your Application
Thermal paste can handle those scorching temps from power-hungry CPUs without breaking down—but it's messier and needs reapplication after a while due to drying out or pump-out effects. Pads? They’re more stable long-term but may not perform as well under extreme heat spikes.When comparing thermal pads vs thermal paste, remember it isn’t always about peak numbers—it’s about matching your cooling solution to the job at hand.
Pros and Cons of Thermal Pads vs Thermal Paste
A quick look at how thermal pads and thermal paste stack up—performance, ease, and long-term use all come into play.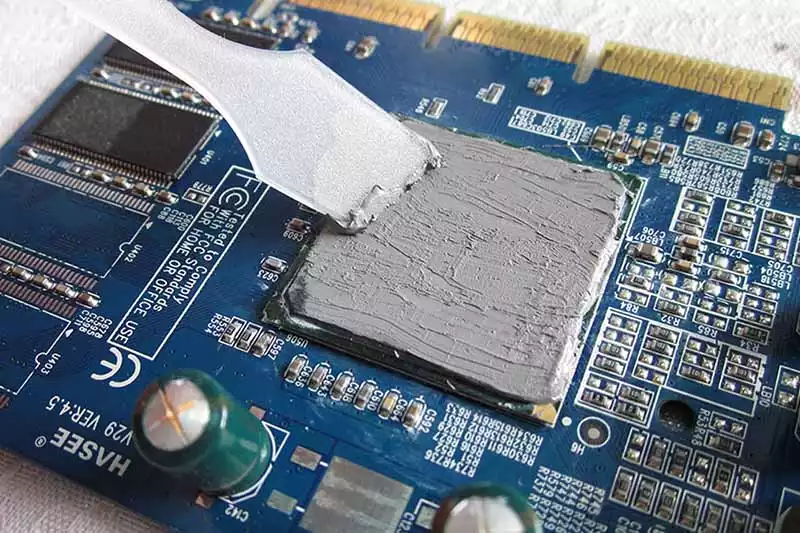
Advantages of Using Thermal Paste for High-Performance Cooling
- Superior performance for CPUs and GPUs where every degree counts
- Fills microscopic gaps between the processor and heatsink with high viscosity, improving heat transfer
- Offers better thermal conductivity than most pads, especially under heavy loads
- Preferred in enthusiast builds due to its ability to prevent thermal throttling during peak performance
Why Thermal Pads Might Be a Better Option for Convenience
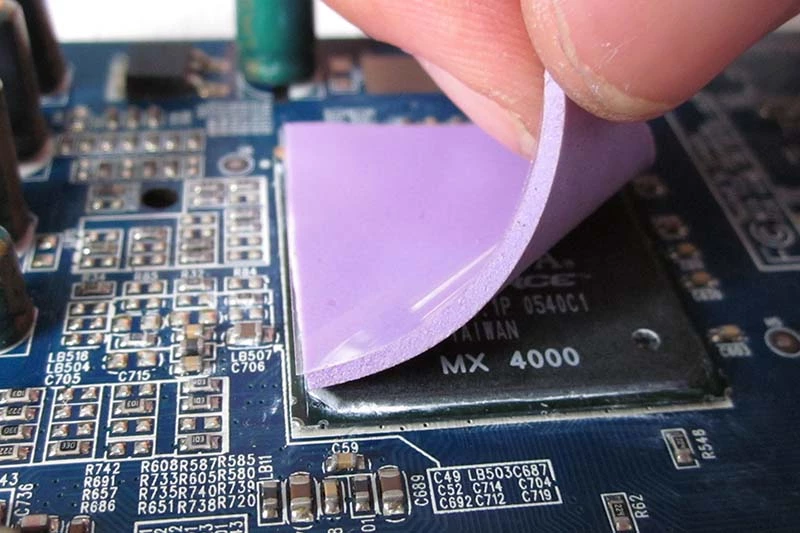
- No mess—just peel and stick; no need for precision like with paste.
- Ideal for beginners or quick maintenance jobs like laptop repairs or replacing old server components.
- Pre-cut options come in various thickness variations, making them versatile across different builds.
- Don’t dry out quickly, offering solid lifespan even in dusty environments.
- Offer natural electrical insulation, reducing risk during installation.
The Trade-off Between Long-Term Stability and Application Ease
For Thermal Pads:- Practically immune to drying out = better long-term material stability.
- Easily removable = ideal for frequent hardware swaps or upgrades.
- Lower chance of poor application = consistent contact across surfaces
- Requires careful spread technique = riskier if done wrong.
- May degrade faster under high heat cycles = needs reapplication over time.
- Can be messy = harder cleanup during maintenance
Real-Life Use Cases Where Choice Matters
- Building a gaming rig? Go with high-performance paste—it’ll help your CPU stay cool even under stress.
- Fixing an older laptop? A pad is your best friend here—quick install, no curing time.
- Upgrading server racks? Pads win again—they're reusable and offer safe insulation near sensitive components.
- Custom loop cooling build? Stick with paste—you’ll get more precise contact and better heat transfer.
How Beginners Can Choose Without Overthinking It
Step-by-step guide:Step 1: Check your component type—CPU/GPU-heavy systems benefit more from good-quality paste.
Step 2: Consider how often you’ll open the system; frequent tinkerers may prefer reusable pads.
Step 3: Match the product’s specs—look at its rated thermal resistance, not just brand hype.
Step 4: Think about your confidence level; if unsure about spreading technique, go with a pad.
Step 5: Always double-check contact pressure post-installation regardless of what you choose.
Choosing between these two isn’t rocket science—it’s about matching needs with features that matter most in real-world setups.
When to Choose Thermal Paste Over Thermal Pads
If you're stuck on the whole "thermal pads vs thermal paste" debate, this guide clears the air for high-performance scenarios.High-Frequency Microprocessors and Thermal Paste
- CPU and high-end processor surfaces often have microscopic irregularities. Thermal paste fills those better than pads.
- For overclocked systems, thermal paste offers superior thermal conductivity, reducing temperature spikes.
- Unlike pads, pastes can be applied with a thinner bond line, maximizing contact between the die and the cooler’s base.
When to Opt for Thermal Paste in Power Electronic Components
Grouped Use Cases Where Paste Outperforms Pads:- High-wattage MOSFETs and GaN transistors benefit from enhanced heat transfer via low-viscosity pastes.
- Devices with uneven mounting pressure need materials that spread evenly—pads can leave gaps; paste doesn’t.
- Applications requiring direct metal-to-metal contact—such as IGBT modules or inverter stages—rely on thin-layered compounds for consistent performance.
How to Apply Thermal Paste for Optimal Performance
Getting the most out of your CPU or GPU starts with nailing the thermal paste application.Surface Preparation Procedures for Effective Thermal Paste Application
Before you even touch the paste, surface prep is key. A clean base equals better heat transfer and longer component life.- Use Isopropyl Alcohol Wipe both the CPU/GPU die and heatsink base with at least 90% isopropyl alcohol using a lint-free cloth or coffee filter.
- Remove Old Residue Thoroughly Scrape off any old thermal paste gently with a plastic tool—metal can scratch surfaces and ruin contact quality.
- Inspect for Imperfections Check both surfaces under good lighting. Any leftover gunk, scratches, or oil from your fingers? Clean again.
- Avoid Touching Surfaces After Cleaning Finger oils are like glue for dust—keep your hands off after cleaning.
- Check Flatness of Heatsink Base Some cheap coolers aren’t perfectly flat. Lay a razor blade across it to see if there’s a gap. If so, don’t expect great results.
- Proper prep doesn’t just make things cleaner—it helps reduce air gaps that mess up heat dissipation between your chip and its cooler.
Applying Thermal Paste: Best Practices for Even Coverage
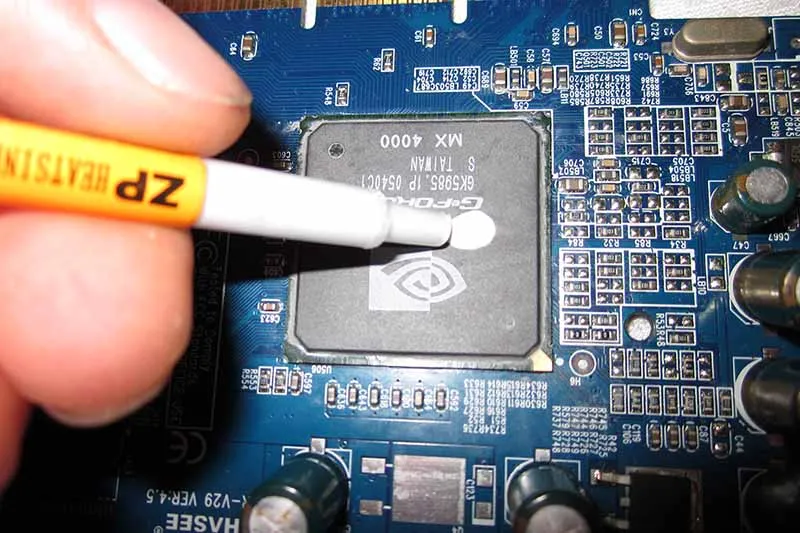

How you apply matters just as much as what you apply. The goal? Smooth coverage without overflow or dry spots.Pea-Sized Dot Method – This classic works well on most CPUs. Just one small blob in the center spreads under pressure.
- Line Spread – For rectangular dies like some Intel chips, a short thin line across the middle ensures better edge-to-edge contact.
- Cross Pattern – For large CPUs like Threadripper, an X-pattern helps reach all corners when compressed by the heatsink.
- Using too much product—it oozes out and insulates instead of cooling.
- Spreading manually with cards or fingers—it introduces air bubbles.
- Reusing old paste—just don’t; it dries out and cracks over time.
Ensuring Proper Adhesion: Techniques for Better Thermal Conductivity
Good adhesion means no trapped air—and that means better cooling when things get hot under pressure.Apply consistent downward pressure during installation so that the heatsink squishes the paste evenly across every millimeter of surface area. Don’t twist it around once it makes contact—that just drags air back in.
Make sure mounting screws are tightened diagonally in alternating corners to balance force evenly across the chip surface—tightening one side too early can lift another side slightly, creating micro gaps invisible to the eye but deadly to thermal transfer efficiency.
In short? You don’t need fancy tools—just patience, steady hands, and even torque on those screws will do more than any expensive compound alone ever could when comparing results in real-world tests between thermal pads vs thermal paste solutions used improperly versus properly applied ones.
Final Thoughts on Thermal Pads vs Thermal Paste
Summary of Thermal Pads vs Paste: Which One Fits Your Needs?
Choosing between thermal pads and thermal paste depends heavily on your setup, budget, and performance needs. Here's a quick comparison to help you sort it out:Material Type & Application
- Thermal paste offers superior heat transfer but requires careful application, especially over CPUs or GPUs.
- Thermal pads are easier to install and great for filling uneven gaps between components.
- Paste generally provides better conductivity, ideal for high-performance builds.
- Pads sacrifice some efficiency but offer solid baseline cooling with less mess.
- Pads can be reused if handled properly; paste often needs reapplying after long-term use due to degradation.
| Use Case | Recommended Option | Reason |
| Gaming PC Builds | Thermal Paste | High-performance cooling needed |
| Laptops | Thermal Pad | Space constraints, ease of handling |
| Office Desktops | Either | Depends on thermal load |
| Consoles | Thermal Pad | Pre-cut sizes simplify installation |
If you're working with an awkward layout or need quick fixes, pads win. But if you're chasing every degree in temps, go with paste.
Key Takeaways: Making the Right Decision for Your Cooling Requirements
There’s no one-size-fits-all when it comes to choosing between these two thermal interface materials. What matters most is matching the right product with your expectations and skill level.- For beginners? Stick with thermal pads—they’re forgiving during installation and provide reliable insulation without fuss.
- For enthusiasts pushing clock speeds? Go for thermal paste—it delivers tighter contact points and better overall heat dissipation.
- For long-term stability? Look at specs like viscosity, curing time, and how frequently you'll need reapplication. If you want plug-and-play simplicity, grab a pad. If you're chasing peak efficiency down to the decimal point, get that tube of paste ready. Either way, understanding what each does best gives you control over your system's cooling game.
FAQs about Thermal Pads vs Thermal Paste
What determines the better choice between thermal pads and thermal paste in large-scale production?A subtle tradeoff of precision and simplicity defines it.
- Thermal Conductivity Performance: Conductive Silicone Paste offers stronger transfer efficiency for CPU Heat Dissipation or GPU Thermal Management.
- Thermal Resistance Characteristics: Pads hold higher resistance but provide consistent placement across Power Electronic Components.
- Electrical Insulation Capability: Pads safeguard Integrated Circuit Packaging during Reflow Soldering Oven operation where insulation is vital.
How does automated equipment influence factory-wide material application?
Digital machines breathe rhythm into volume work—maintaining quality under pressure:
- The Automated Dispensing System ensures uniform feeding of Heat Conductive Compound along complex chip arrays.
- Screen Printing Equipment spreads the Phase Change Material swiftly across Printed Circuit Board Assembly lines with controlled thickness tolerance.
- Combined with a strict Quality Control Inspection, they minimize waste while maintaining adherence to IPC Standard Conformity standards.
Why do industrial designers often prioritize pastes inside performance-driven systems?
Inside power-hungry engines like High-Frequency Microprocessors and amplifiers:
★ Pastes adapt flexibly over uneven metal surfaces through Adhesion Promotion Techniques without extra machining work.
★ Their natural flow fills microscopic gaps under Power Amplifier Cooling needs before entering a Material Curing Schedule cycle monitored by temperature sensors.
This fluid contact yields powerful synergy between surface finish and Long-Term Stability Reliability ratings.
Which international standards define acceptable materials for mass order use?
The global supply chain translates safety into exact codes:
| Standard | Focus Area | Example Implementation |
| RoHS Compliance Certification | Restricts hazardous elements | Used during LED Thermal Conductivity module approval |
| REACH Regulation Adherence | Governs chemical properties | Guides Conductive Silicone Paste imports into EU |
| UL Flammability Rating | Fire safety threshold control | Applied on pad-based insulation layers over IC Package Heat Transfer zones |
Each certification solidifies trust—ensuring every Thermal Interface Material performs safely inside demanding electrical environments worldwide.

 English
English
 usheenthermal
usheenthermal



