Thermal Putty vs Thermal Pads: Uncover the Ultimate Cooling Solution
Not all heroes wear capes—just as thermal putty comes in syringe or sheet form, yet still fights against high temperatures like a champion inside electronic devices. This is the silent glory of thermal putty, a viscous "genius" that can seep into every gap between the heat-generating chip and the heat-dissipating metal. But then you’ve got thermal pads—clean-cut, quick to apply.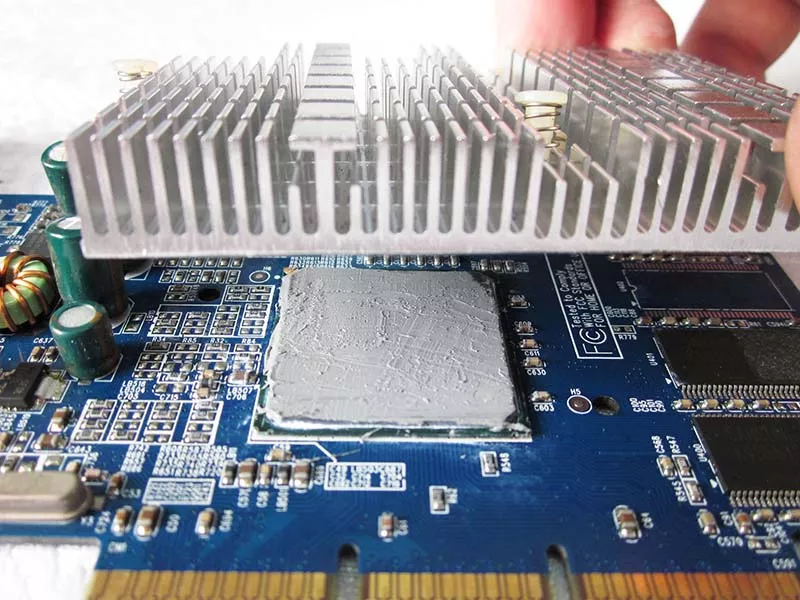
Choosing between them ain’t just an engineer’s headache—it’s a supply chain chess match. Thermal materials are more than just filler—they’re frontline soldiers in the war against premature failure. Picking wrong? That could mean higher return rates and warranty claims stacking up faster than coffee cups at 2 AM on deadline night.
Essential Insights on Thermal Putty for Optimal Cooling Solutions
➔ Thermal Interface Material Importance: Thermal putty serves as a crucial thermal interface material, enhancing heat transfer efficiency between components and significantly reducing thermal resistance.
➔ Composition Characteristics: Made from a viscous compound, thermal putty is moldable and adaptable, allowing it to fill gaps effectively in various applications.
➔ Performance Metrics: With low thermal resistance, thermal putty is particularly advantageous in high-performance scenarios, ensuring efficient dissipation of heat from sensitive components.
➔ Quality Control Standards: Regular quality checks for thermal putty ensure long-term consistency and reliability, making it a dependable choice in critical systems.
➔ Application Techniques: Precise application techniques, including surface preparation and automated dispensing, are essential for maximizing the effectiveness of thermal putty in cooling solutions.
Understanding Thermal Putty: A Key Cooling Component
Getting your PC thermals under control? Let’s break down how thermal putty and its cousins keep things chill—literally.The Role of Thermal Interface Material in Heat Management
- Thermal interface materials—aka TIMs—bridge the microscopic air gaps between hot components and coolers.
- This means smoother heat transfer, lower system temps, and longer hardware life.
- Without TIMs like thermal grease or putty, even high-end cooling setups fall flat.
Essential Applications of Thermal Putty in High-Performance Computing
You’ll find thermal putty doing the heavy lifting inside gaming rigs, AI servers, and rendering farms:- CPUs & GPUs – Keeps hot silicon from throttling under load.
- Memory modules – Handles uneven surfaces better than pads.
- VRMs & power ICs – Maintains contact even when pressure shifts.
| Application Area | Surface Type | Recommended TIM | Typical Temp Range |
| GPU Core | Flat | High-conductivity Thermal Pad or Thermal Putty | Up to ~90°C |
| VRM Modules | Uneven/angled | Thermal Putty | Up to ~105°C |
| RAM Heatsinks | Irregular | Thermal Pad | Up to ~85°C |
This flexibility gives thermal putties a serious edge when things get cramped or oddly shaped under the hood.
5 Key Differences Between Thermal Putty And Thermal Pads
Ever wondered what sets a squishy thermal compound apart from a solid pad? These five core differences break it down—fast, clean, and easy.Thermal Putty vs Thermal Pad: Technical Composition
.webp)
.webp)
Material Type
- Thermal putty: A moldable, paste-like substance that can be squeezed into tight spaces.
- Thermal pad: A solid-state material pre-cut for uniform application.
- Putty adapts to odd shapes and uneven contours.
- Pads stick to flat surfaces best and don't stretch or compress much.
- If you're dealing with custom hardware or inconsistent gaps, go with the putty.
- For standard heatsinks or GPUs, pads are usually more than enough.
Performance Metrics: Low Thermal Resistance Comparison
When it comes to raw numbers, there's one clear winner for hardcore cooling jobs:| Material Type | Thickness Rating mm |
TyThermal conductive W/m·K |
Thermal resistance@30psi,1mm ℃*in²/W |
Contact Resistance |
| Silicone Thermal Pad | 0.3~10 mm | 1.5~15 | 0.1~0.9 | Moderate |
| Thermal Putty | Variable | 1~5 | 0.02~0.04 | Very Low |
Put simply, if you're chasing peak performance on high-wattage CPUs or GPUs, a quality thermal putty will outperform even top-tier pads thanks to its lower overall thermal resistance, better surface conformity, and superior heat transfer capabilities across uneven surfaces.
Application Tooling: When to Use Each Option
- Thermal Pad: no tools needed,they're peel-and-stick simple. Always test-fit pads before final placement.
- Thermal Putty: Putty demands careful handling; typically dispensed via syringe or automated systems. With putties, avoid overapplication—it can ooze out during mounting.
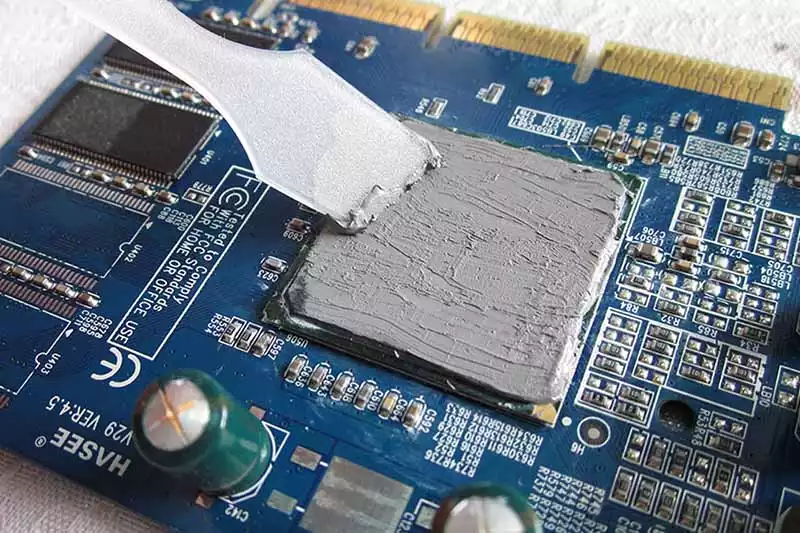

If you're looking for pure ease of use with minimal mess and zero cleanup concerns during installation, pads keep things neat. But when you need precision gap filling under pressure-sensitive components? That’s where the flexibility of thermal putties shines—even if it takes longer to apply right.
Resin Characteristics: Curing Support for Thermal Interface Materials
Unlike their pre-cured counterparts, some types of thermal putties use reactive resins that require curing after application—either at room temperature over time or through controlled heating cycles. This curing process helps them form a semi-solid state that enhances long-term stability without sacrificing their ability to fill microgaps. On the flip side, thermal pads skip this step entirely; they're ready out of the package and stay consistent throughout their lifespan unless exposed to extreme temperatures beyond spec limits.Shelf Life Considerations in Thermal Management Solutions
Here’s what you need to know before stocking up:Thermal Putty
- Typically lasts around 6–12 months unopened if stored properly.
- Exposure accelerates breakdown due to air moisture or separation of filler/resin components.
- Requires airtight containers and cool storage conditions.
- Shelf life often exceeds two years when kept sealed.
- More resilient against environmental factors like humidity or minor heat exposure.
How Thermal Putty Improves Long-Term Thermal Management
No fluff—just facts on how thermal putty keeps your gear cool and running smooth.Enhancing Heat Dissipation in CPU Coolers with Thermal Putty
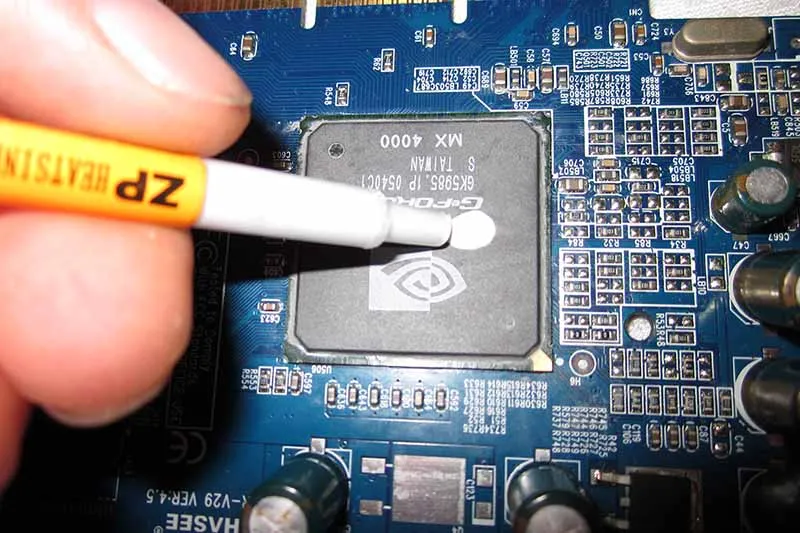

- Gap elimination: The squishy nature of thermal putty lets it seep into microscopic air gaps between the CPU heat spreader and heatsink base, killing off thermal resistance.
- Adaptive flow: Unlike rigid materials, it adapts to uneven surfaces, improving contact without stressing components.
- Improved cooling performance: Better contact means lower temps, especially under high-load conditions like gaming or rendering.
- Durability over time: It resists drying out or cracking even during constant heating cycles.
- Flexible reapplication: It can be reworked without major messes or component damage.
Quality Control Checks for Long-Term Reliability
You wouldn’t trust a parachute that wasn’t tested—same goes for your cooling materials. Manufacturers run every batch of thermal putty through rigorous testing:- Viscosity checks ensure proper flow at room temp and elevated temps alike.
- Curing times are controlled so it doesn’t harden prematurely or stay mushy forever.
- Measured against standard benchmarks for consistent thermal conductivity across batches.
Surface Preparation Techniques for Optimal Thermal Contact
Clean surface = cool system. Here’s how you get there:- Wipe both surfaces using isopropyl alcohol (90%+). No putty, no dust—just clean metal.
- Smooth rough heatsinks using fine-grit sandpaper if needed; pits kill performance.
- Avoid touching cleaned areas with bare fingers—skin oils wreck adhesion fast.
Operating Temperature Range: Ensuring Stability Over Time
Not all compounds hold up when things get hot—or cold.1️⃣ Most quality thermal putties operate between –50°C and +150°C without breaking down.
2️⃣ Even during rapid-fire workloads or idle cooldowns, their viscosity stays stable enough to prevent pump-out effects.
| Material Type | Min Temp (°C) | Max Temp (°C) | Conductivity (W/m·K) |
| Silicone Thermal Pad | –30 | +120 | 1–3 |
| Carbon Fiber Thermal Pad | -50 | +160 | 15-45 |
| Graphite Sheet | –40 | +130 | 20–30 |
| Thermal Putty | –50 | +150 | 1–5 |
| Phase Change Material | –40 | +125 | 3–8 |
That wide range means you’re covered whether you're freezing sensors outdoors or pushing CPUs indoors—reliably stable across seasons and stress tests alike.
Maximize Cooling Efficiency: Thermal Putty Vs Pads
Keeping electronics cool isn’t just about fans and airflow—it’s about what sits between your chips and heatsinks. Let’s break down how thermal putty stacks up against pads.Thermal Putty vs Thermal Pad: A Performance Review
| Thermal Putty | Thermal Resistance(@30psi) ℃*in2/W |
Thermal Conductivity W/m·K |
Viscosit (Pa·s)@25℃ |
Operating temp ℃ |
| SG560-10 | 0.04 | 1.0 | 150 | -50~150 |
| SG560-20 | 0.035 | 2.0 | 200 | -50~150 |
| SG560-30 | 0.02 | 3.0 | 240 | -50~150 |
| SG560-40 | 0.017 | 4.0 | 350 | -50~150 |
| SG560-50 | 0.015 | 5.0 | 400 | -50~150 |
| Siliocne Thermal Pad |
Thermal Resistance@30psi,1mm ℃*in²/W |
Thermal Conductivity W/m·K |
Flame Rating UL 94 |
Operating Temp ℃ |
| SF100 | 0.90 | 1.5 | V-0 | -50~200 |
| SF300 | 0.70 | 2.0 | V-0 | -50~200 |
| SF400 | 0.50 | 2.5 | V-0 | -50~200 |
| SF500 | 0.45 | 3.0 | V-0 | -50~200 |
| SF600 | 0.35 | 5.0 | V-0 | -50~200 |
| SF700 | 0.25 | 7.0 | V-0 | -50~150 |
| SF800 | 0.22 | 8.0 | V-0 | -50~150 |
| SF1000 | 0.18 | 10.0 | V-0 | -50~125 |
| SF1200 | 0.15 | 12.0 | V-0 | -50~125 |
| SF1500 | 0.10 | 15.0 | V-0 | -40~120 |
- Thermal conductivity is the name of the game, and thermal putty usually wins it with lower thermal resistance, making it a go-to for high-performance builds.
- Pads are easy to slap on, but they often leave micro gaps due to poor interface contact—something that putty handles better with its flowable nature.
- If your setup needs precision, like in tight CPU or GPU zones, putty offers better gap filling, especially when components aren’t perfectly flat.
Evaluating Long-Term Stability and Reliability
Let’s be real—nobody wants to crack open their rig every six months because their thermal pad dried out or shifted.
- Thermal putty, being non-curing, stays flexible over time—even through wild temp swings from gaming marathons or heavy rendering loads.
- Pads tend to harden or degrade after repeated heat cycles, reducing their effectiveness over time.
Automated Dispensing Systems for Efficiency in Application
Automated systems are changing the game for how we apply cooling materials:- They ensure consistent layer thickness across multiple units.
- Reduce human error—no more uneven blobs or messy re-dos.
- Improve material use efficiency by minimizing waste during application.
FAQs about Thermal Putty
What makes thermal putty suitable for high-performance computing applications?It molds into every tiny gap between CPU coolers or GPU heat sinks, wrapping Integrated Circuits like a glove to cut down on every fraction of thermal resistance.
- Holds its Thermal Conductivity across extreme Operating Temperature Ranges—perfect for sustained High-performance Computing demands.
- Pairs smoothly with Automated Assembly Lines using Precise Application tools, so each microprocessor feels the same even pressure and cooling touch.
How does the technical composition of thermal putty differ from thermal pads?
Thermal Putty is a pliable Heat Dissipation Compound meant to conform to uneven contact zones; Thermal Pads are rigid pre-cut pieces for flat surfaces.
Can surface preparation impact the effectiveness of thermal interface material?
Dust or oxidation stands like a wall between your heat path and escape. Careful Surface Preparation turns that barrier into open road:
- Clean metallic faceplates until they reflect light evenly.
- Remove microscopic film layers before Curing Process begins.
- Match Density Requirements during application on Power Modules and Voltage Regulators.
What quality control checks help ensure reliable supply of bulk-ordering customers using thermal putty solutions?
For buyers running LED lighting lines or power electronics plants, reliability feels personal—you can’t afford uneven cooling across Memory Chips:
- Viscosity Control tests keep flow consistent through Dispensing Equipment nozzles.
- Density readings confirm compliance before packaging drums roll out the door.
- Simulated heat trials push TIM through full Operating Temperature Range till High Reliability is proven under stress cycles in Testing Equipment labs.

 English
English
 usheenthermal
usheenthermal



